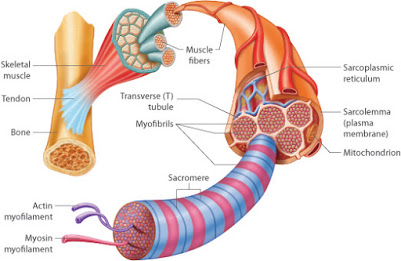
SKELETAL MUSCLE
•Muscle mass :
– Skeletal Muscle mass is made up of large number of individual muscle cells or myocytes.
-Myocytes are long and slender in appearance and are commonly called muscle fibers.
-Muscle fibers are arranged parallel to one another with some connective tissue in between and they are multinucleated.
– Fascia separates muscle mass from its neighboring tissues.
– Epimysium is a connective tissue sheath which covers the muscle beneath the fascia.
-In the muscle , the muscle fibers are arranged as bundles or fasciculi.
– These fasciculi are covered by perimysium .
– And endomysium is the layer which covers each muscle fibers.
• Muscle fiber :
-These are cylindrical in shape and are 3cm in length.
– Muscle fibers are attached to tendon which in turn attaches to the bones.
– Plasma membrane encloses each muscle fiber that lies beneath the endomysium and also called as sarcolemma.
-Sarcoplasm is the cytoplasm of the muscle.
* Structures present within the sarcoplasm are ;
(1) nuclei
(2) myofibrils
(3) mitochondria
(4)sarcoplasmic reticulum
(5) Golgi apparatus
(6) ribosomes
(7) glycogen droplets
(8) occasional lipid droplets .
– Nuclei are situated just beneath the sarcolemma and are oval or elongated .
– Each muscle fiber has one or more number of nuclei and in long muscle fibers many nuclei are present.
• Myofibril
√ Definition :
-These are the fine parallel filaments seen in sarcoplasm of the muscle cell.
√ Morphology :
– In muscle fiber cross section, the myofibrils are appears like a distinct dots within sarcoplasm.
– And these myofibrils are run along the entire length of muscle.
– Cohnheim’s areas are the fields where some of the myofibrils are arranged in groups .
√ Microscopic structure of a Myofibril :
– All the myofibrils are consists of a number of two alternative bands and are alled as the sections , segments or disks.
– Bands are formed by the muscle proteins.
– The two bands are;
(1) light band / ‘I’ band
(2) Dark band / ‘A’ band.
1) Light band
– Light band is isotropic to polarized light hence it is called as isotropic or I band.
– When this polarized light passes through the muscle fiber at ‘I’ band area , the light rays are refracted at the same angle.
2) Dark band
-Dark band is anisotropic to polarized light , hence it is called as anisotropic or A band .
-When this light passes through muscle fiber at this area , the light rays are refracted at different directions .
-When this light passes through muscle fiber at this area , the light rays are refracted at different directions .
– It is also called as ‘ Q’ disk.
• Sarcomere
√ Definition :
– It is the structural and functional unit of the skeletal muscle.
-Also known as basic contractile unit of the muscle.
√ Extent :
– It extends between two ‘Z’ lines of myofibrils.
-The average length when muscle is in relaxed state is 2- 3 micro.
√ Components :
(1) one half of light ‘I’ band
(2) one dark ‘A’ band
(3) one half of light ‘I’ band.
– ‘H’ zone is the light area present in the middle of ‘A’ band
– ‘M’ line is the middle part of myosin filament lies in the middle of ‘H’ zone and this line is formed by the myosin binding protein.
•Electron microscopic study of Sarcomere:
– Myofilaments are the thread like structure present in the Sarcomere.
-They are of two types
(1) Actin filaments : Thin filaments
(2) Myosin filaments : Thick filaments.
• Contractile proteins of muscle:
1) Myosin molecule
2) Actin molecule
3)Tropomyosin
4)Troponin
1) Myosin molecule :
– About 200 myosin molecules are present in each myosin filament.
– Two portions of myosin molecule;
✓ Tail portion
✓ Head portion
Tail portion :
– Formed by heavy chains and both the heavy chains are twist around each other as a double helix.
Head portion :
– Formed by the heavy chains and light chains.
– Both the heavy chains turn away in opposite directions at one end of the double helix and form the globular head portion.
– Each part of the head portion of myosin molecule consists of two light chains.
✓ essential light chain : regulate structural stability of myosin head
✓ regulatory light chain : regulates kinetics of myosin head.
– There are two attachment sites in each myosin head .
– One is for actin filament attachment
Another one is for ATP molecule attachment.
2) Actin molecule :
– Each actin molecule is called as F-actin and they are the major constituents of the thin actin filaments.
– It is a polymer of G-actin .
3) Tropomyosin:
– In the double helix strand of actin filament consists of about 40 to 60 Tropomyosin molecules.
– And in relaxed condition of the muscle, these molecules cover all active sites of the F-actin molecules.
4) Troponin :
– It includes three substitues,
(1) Troponin I : attached to F- actin
(2) Troponin T : attached to Tropomyosin
(3) Troponin C : attached to calcium ion.
* Other proteins of the muscle ;
(1) Actinin – attaches actin filaments to ‘Z’ line
(2) Desmin – attaches ‘Z’ line with sarcolemma.
(3)Nebulin – runs in parallel to actin filaments
(4) Titon – connects ‘M’ line and ‘Z’ line.
• Sarcotubular system :
– It is a system of membranous structure in form of the vesicles and the tubules in sarcoplasm of muscle fiber .
– Myofibrils are surrounded by the Sarcotubular system .
* This system is formed by the 2 types of structures ;
(1) T- tubules
(2) L- tubules.
1) T- tubules :
✓ Transverse tubules are formed by the invagination of sarcolemma and they are narrow tubules.
✓These tubules penetrate from one side of the muscle fiber to another side.
✓ The T- tubules open to the exterior of the muscle cell and therefore , the ECF runs through their lumen .
2) L- tubules :
✓These are the closed tubules which runs in the long axis of the muscle fibers and form sarcoplasmic retinaculum.
✓L- tubules do not open to exterior of the muscle cell.
✓ At regular intervals , the L- tubules dialates to form terminal cisternae.
✓ Terminal cisternae is in close contact with T- tubules.
✓ On either side , T- tubules along with the cisternae is called the triad of skeletal muscle.
✓ In human skeletal muscle , these triad are situated at the junction between Anisotropic band and isotropic band.
✓ Calcium ion are stored in L- tubules and are more in cisternae.
• Functions of Sarcotubular system:
(1) T- tubules :
– This tubules are responsible for the rapid transmission of the nerve impulse to form the action potential from sarcolemma to the myofibrils.
(2) L- tubules :
– This tubule stores large number of calcium ions.
– When the action potential reaches the cisternae of the L- tubules , calcium ions are releases into the sarcoplasm.
FOLLOW ME IN SOCIAL MEDIATHANK YOU.



Pingback: ELECTROMYOGRAM AND DISORDER OF SKELETAL MUSCLE - PHYSIOFEEDS